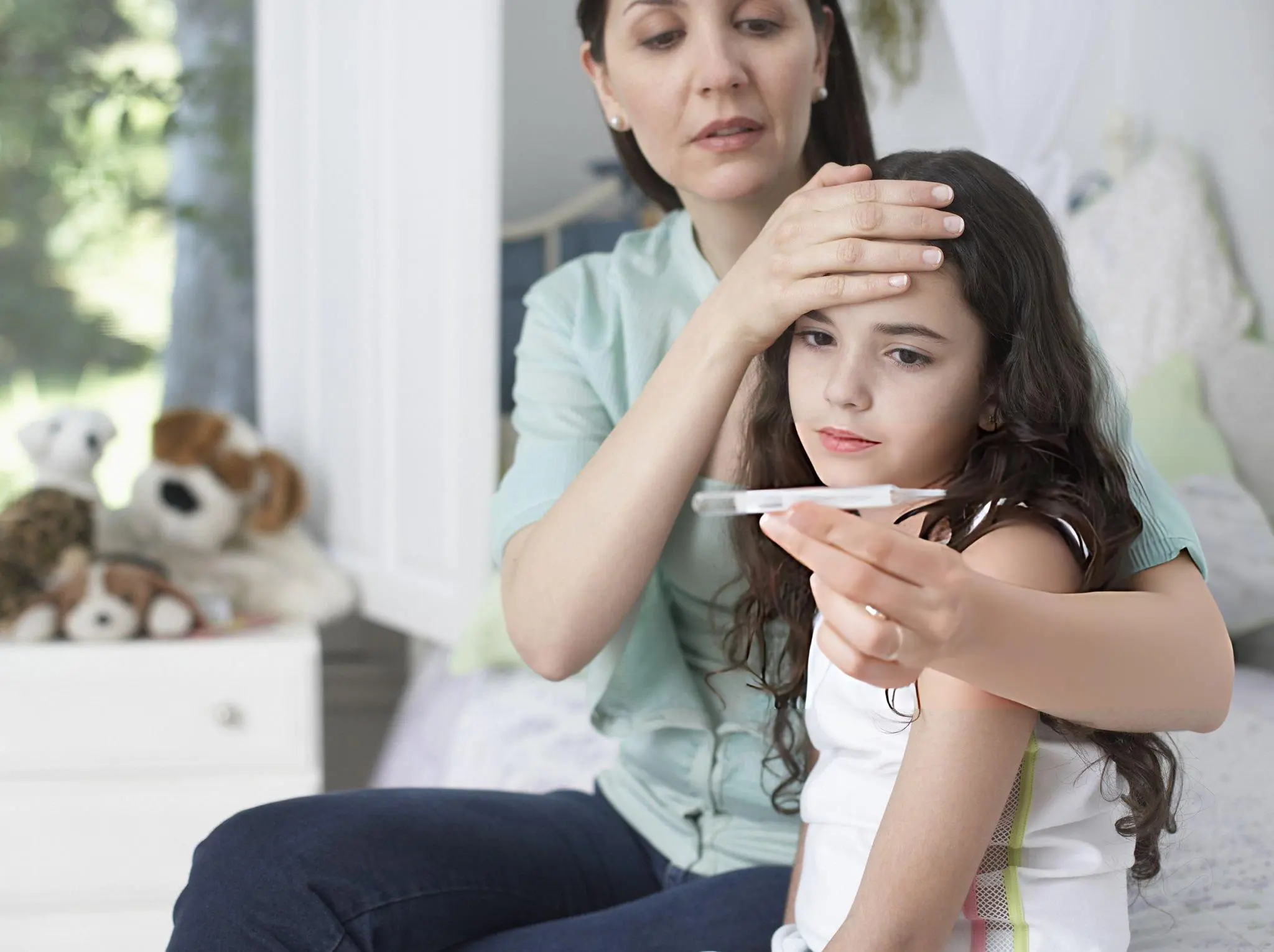
Young children tend to get sick a lot because their immune systems are still developing and they come into contact with many other kids. Some are mild, others can complicate the disease if untreated. Parents, teachers and caregivers need to recognize these conditions and help to prevent them.
Common Childhood Illnesses
Cold and Flu
Common cold and flu spread through coughing, sneezing and touching contaminated surfaces. Common symptoms are fever, sore throat, cough and fatigue. As schools and daycare centers remain open, kids are inevitably going to catch these infections.
Prevention Tips:
- Teach children to wash their hands with soap.
- So keep them away from sick people.
- Do give them a balanced diet to increase immunity.
- Promote vaccination against flu for additional safety.
Ear Infections
Children suffer frequent ear infections because they have small ear canals. They lead to ear pain, fever and difficulty sleeping.
Prevention Tips:
- Keep the ears dry after swimming or bathing.
- Do not expose children to cigarette smoke, which raises the risk.
- Make sure children are up to date on routine vaccinations.
Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
Gastroenteritis leads to diarrhea, vomiting, and dehydration. It can be transmitted through contaminated food and water.
Prevention Tips:
- Wash hands after going to the bathroom and before eating.
- Do not provide children food obtained from unsafe sources.
- If they have symptoms, make sure children drink plenty of fluids.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
The viral infection causes fever, sores in the mouth and rashes on the hands and feet. It is transmitted in daycare centers and schools through direct contact.
Prevention Tips:
- Regularly wipe down toys and surfaces.
- Instruct children never to share drinks and cutlery.
- Do not send infected children to school until they are well.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox results in blistering, itchy spots, fever, and fatigue. It is transmitted through the air and direct contact.
Prevention Tips:
- Long-term protection only comes with vaccination.
- Keep your distance from people with the virus.
- Trim nails to avoid scratching and infections.
Asthma
Asthma is a disease in which airways become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. Examples: Dust, pollen, cold air.
Prevention Tips:
- Recognize and stay away from triggers.
- Take inhalers prescribed, as needed.
- Home cleaning should be dust-free.
Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR)
These viral infections can lead to fever, rashes, swollen glands and serious complications in some people.
Prevention Tips:
- The MMR vaccine is used against these diseases.
- Parents should have their children up to date on all routine vaccinations.
- Do not touch sick people
How to Stop These Illnesses
Hygiene and Cleanliness
- Teach them to wash their hands after using the bathroom and wash before meals.
- Disinfect surfaces that are often touched, like toys, doorknobs and tables.
- Promote good cough hygiene (cough into the inside of your elbow)!
Strengthening the Immune System
- Offer children healthy portion sizes, inclusive of fibers, aquatics, amino acids, etc.
- Make sure to allow enough sleep for proper growth and immunity.
- Promote outside play and physical activity to enhance overall wellbeing.
Safe School and Daycare Practices
- Schools should have appropriate ventilation and cleanliness.
- Otherwise, sick children should remain at home until they are better.
- Teachers and caregivers ought to keep an eye on symptoms and step in early.
Seeking Medical Help When Needed
- A fever over 100.4°F (38°C) that doesn’t go away needs treatment.
- Signs of an emergency are difficulty breathing, severe dehydration or loss of consciousness.
- Parents should see a doctor if a child’s symptoms do not improve in a few days.
If you’d like professional advice or follow‑up for your child’s symptoms, get in touch with our experienced Wallsend GP team at our main site.
The Role of Telehealth in Childhood Illnesses
Telehealth services enable parents to communicate with doctors without going to a clinic. This minimizes exposure to other sick people and offers quick medical advice.
Benefits of Telehealth:
- Immediate access to doctors for minor illnesses.
- Prescriptions and treatment plans without waiting at clinics.
- Guidance on when a child needs in-person care.
Conclusion
Hygiene, nutrition, vaccines and prompt treatment when necessary are key to preventing childhood illnesses. Parents, caregivers and educators all help keep children healthy. Many infections can be prevented and children can be grown with robust immune systems by the following preventive measures.